Sponge divers pulled the to start with fragments of what grew to become identified as the Antikythera Mechanism from a Roman-era shipwreck in 1901 off the coastline of the Greek island Antikythera. At any time since the discovery, experts and historians have continued to search for additional artifacts from the shipwreck although also piecing alongside one another the story of what is generally regarded the world’s 1st laptop.
Scientists figured out yrs ago that the product was a bronze astronomical calculator that may have served the historical Greeks monitor the positions of the sun and the moon, the lunar phases and even cycles of Greek athletic competitions. Researchers documented in 2021 they had made the very first comprehensive electronic product of the so-identified as Cosmos panel of the 2,000-year-aged mechanical machine. And they uncovered a properly-preserved skeleton of a young gentleman (possibly aspect of the ship’s crew) that could offer the to start with DNA evidence from the sunken boat. The 82 corroded steel fragments of the mechanism also include inscriptions that researchers have ongoing to decipher. Here is a glimpse at the mysterious unit and info scientists have uncovered about it.
Corroded panel
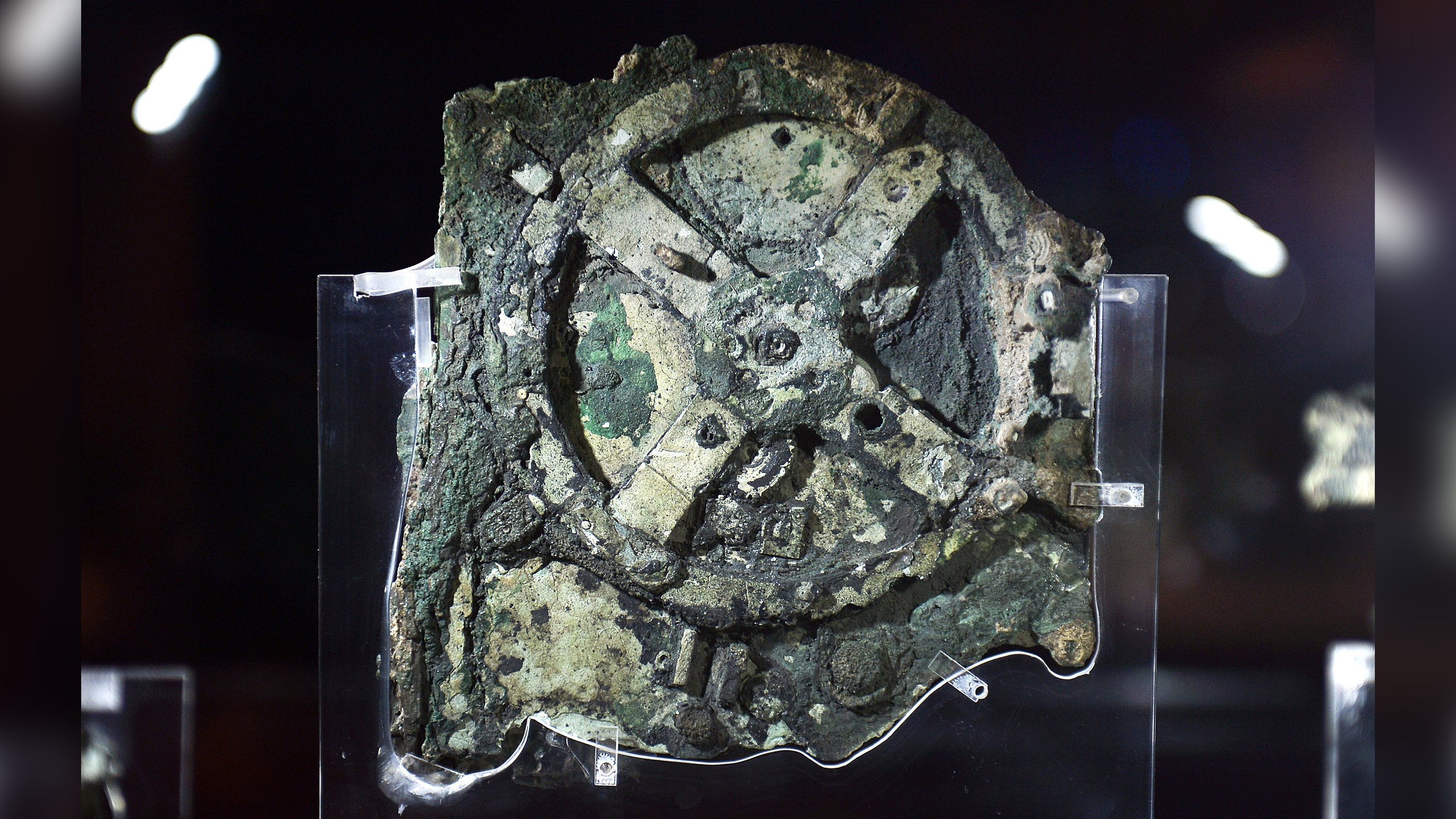

The most properly-known piece of the Antikythera Mechanism is demonstrated at the Archaeological Museum in Athens. The contraption held 37 interconnected gears that scientists uncovered would have helped historical individuals to comply with heavenly bodies.
Hand-cranked computer

The Antikythera system, shown right here in this personal computer reconstruction, was about the dimensions of a shoebox, with dials on its exterior and an intricate process of 30 or so bronze equipment wheels within. Though it was located in a number of corroded fragments, researchers have applied imaging and other technologies to piece the device with each other and even decode its inscriptions. When it was in use, a consumer of this “laptop or computer” could have turned a hand crank and tracked the positions of the sun and the moon, the lunar phases, and even cycles of Greek athletic competitions
.
Exosuit
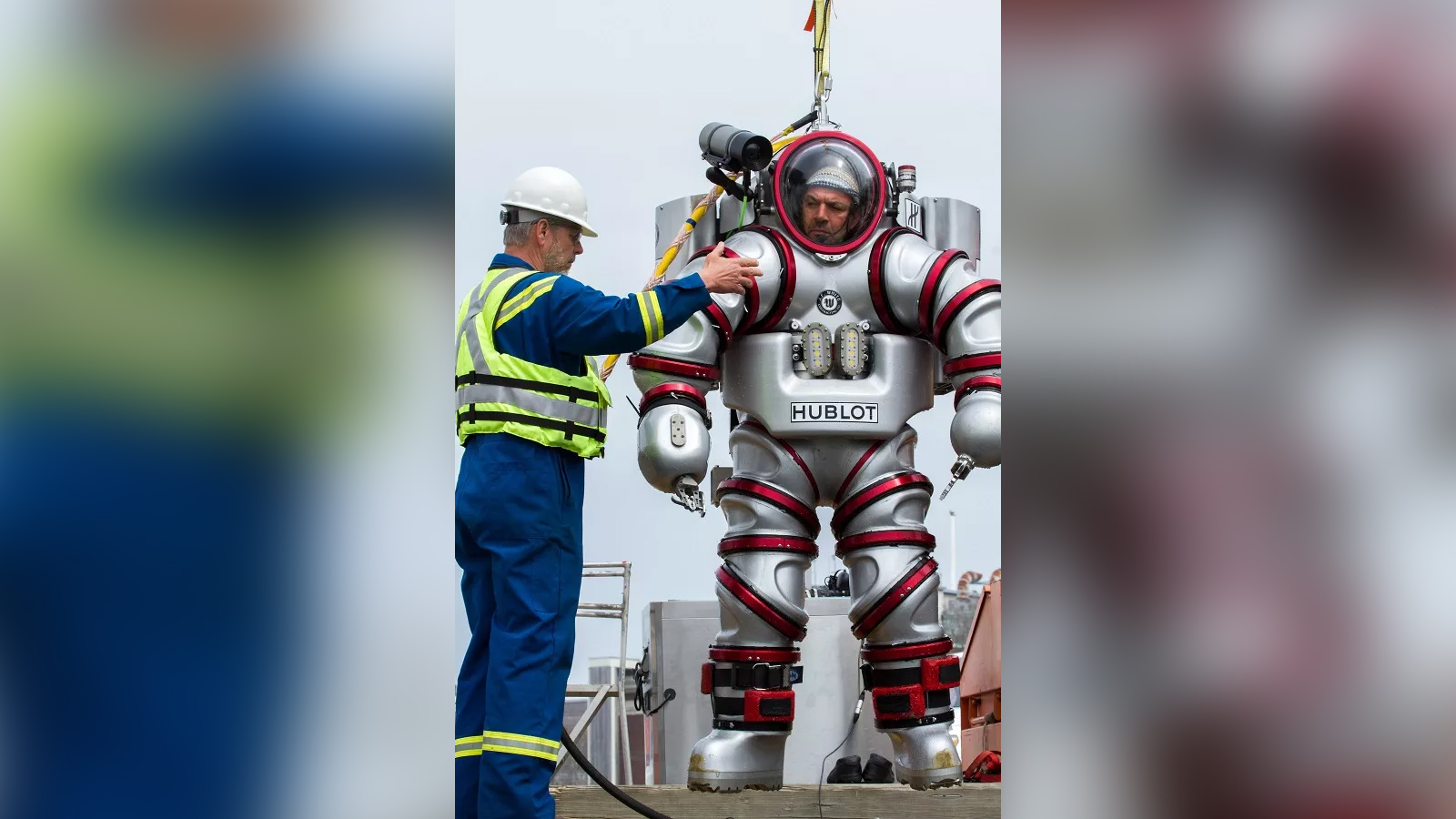

In September 2014, researchers explored the Antikythera shipwreck, seeking for sunken statues, gold jewelry and other historical artifacts shed in the Agean Sea. For the mission, they used the Exosuit that authorized the operator to safely and securely descend hundreds of feet down below the surface of the Aegean Sea.
Shipwreck dive
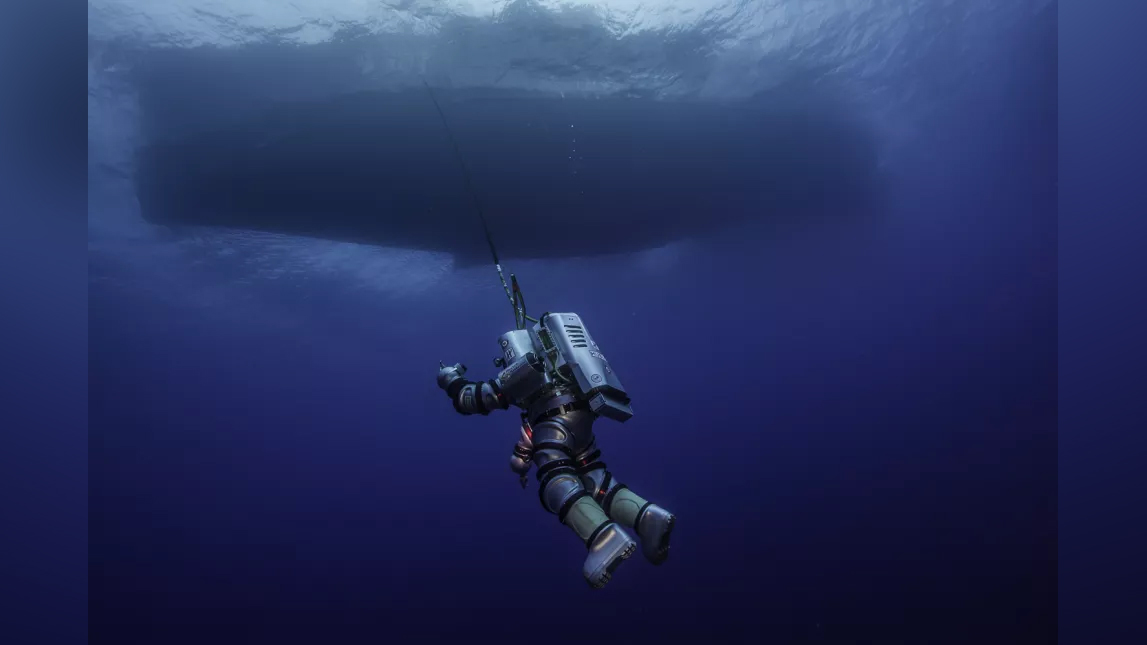

Phil Shorter piloted the Exosuit near the end of the “Return to Antikythera” mission, which lasted from Sept. 15 to Oct. 7, 2014.
Getting artifacts
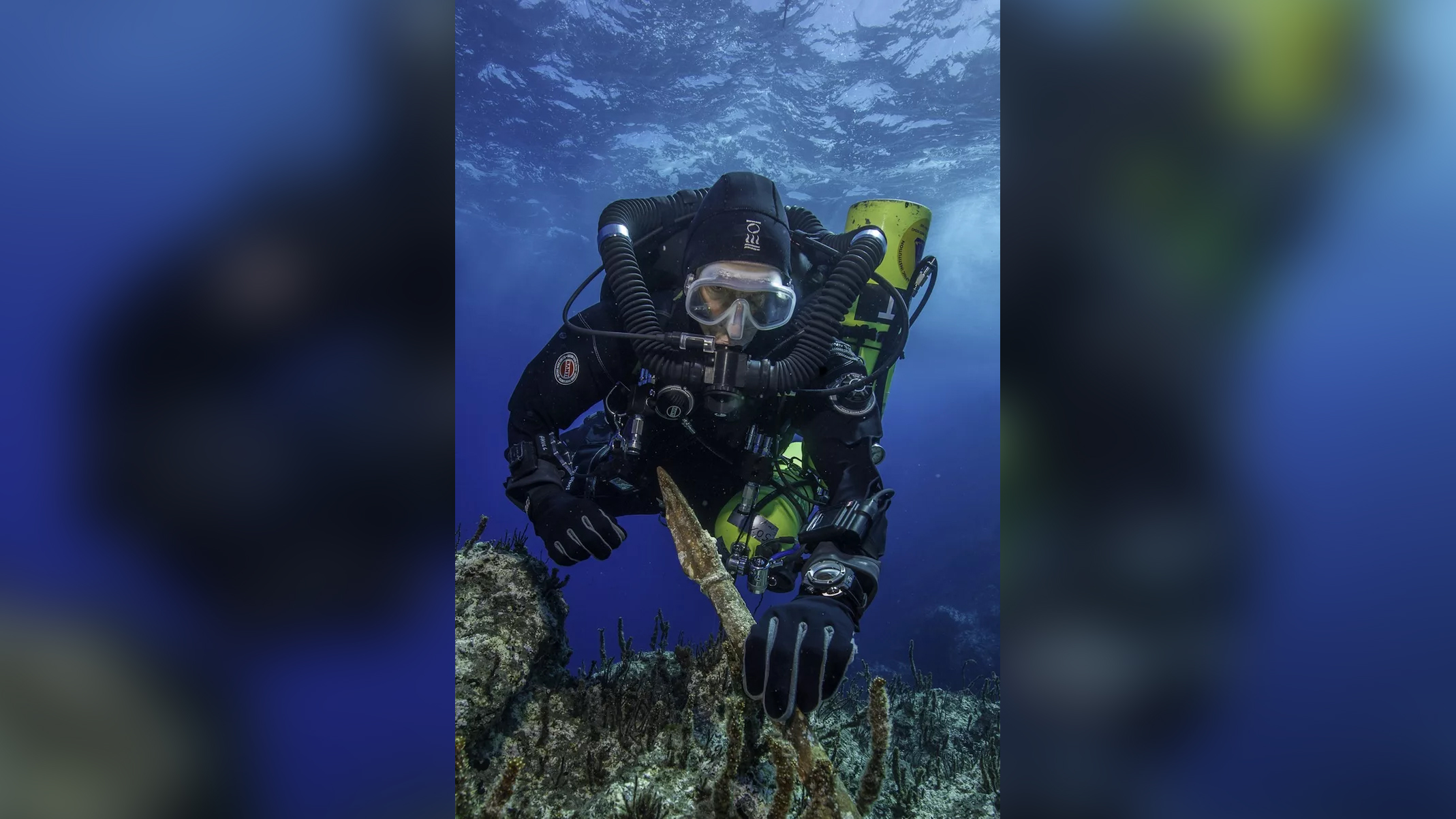

Throughout the dive close to the shipwreck, scientists found a bronze spear. The spear would have been far too huge and significant to be a functional weapon 2,000 decades back, and so it probable was element of a statue, the scientists claimed.
Large haul
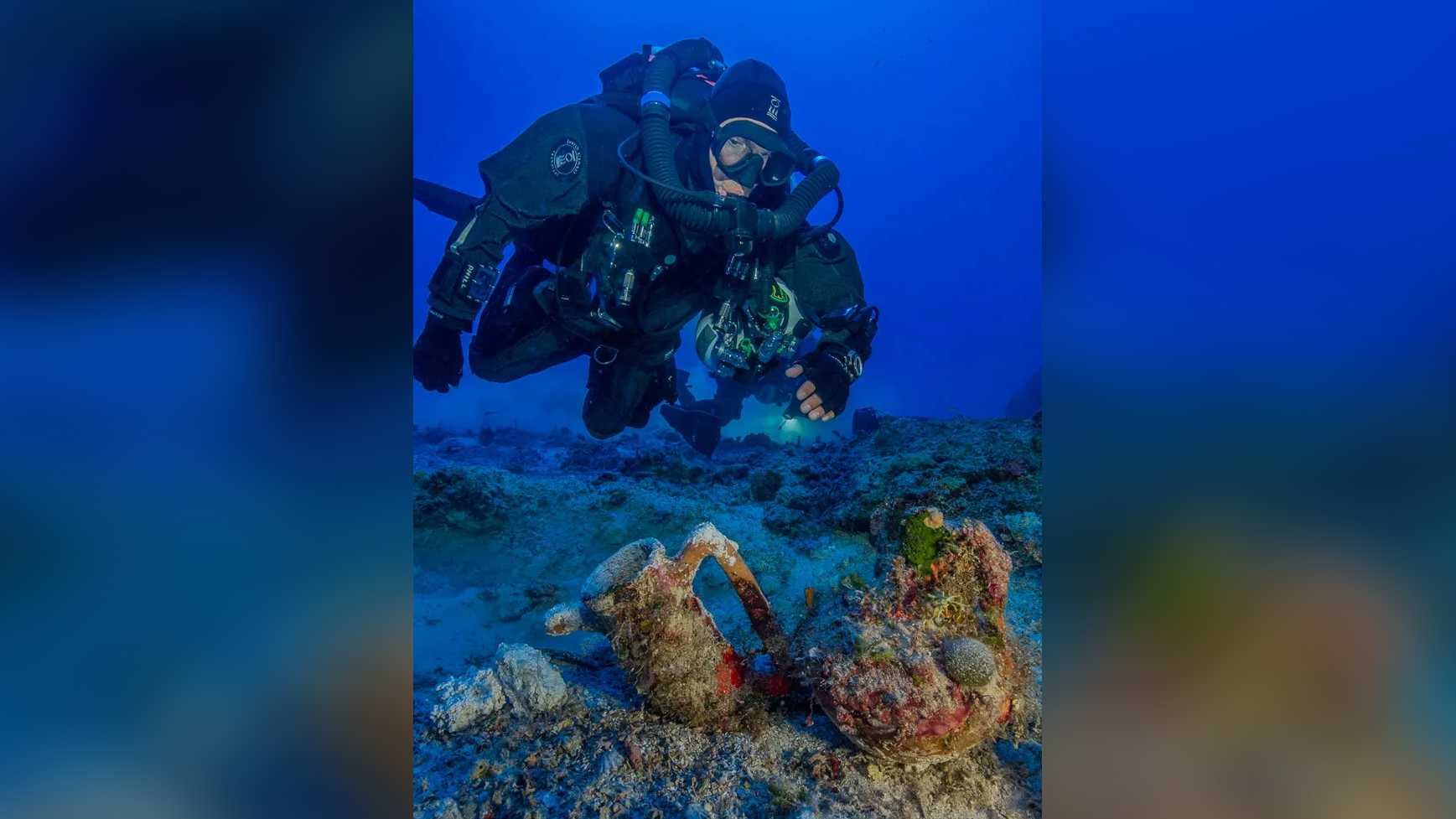

Listed here, an archaeologist swims about artifacts at the internet site of the Antikythera shipwreck. A trove of artifacts have been located associated with the shipwreck. In 2015, researchers pulled up 50 objects from the depths as component of their scientific excavation of the Antikythera wreck web site.
Wine decanter
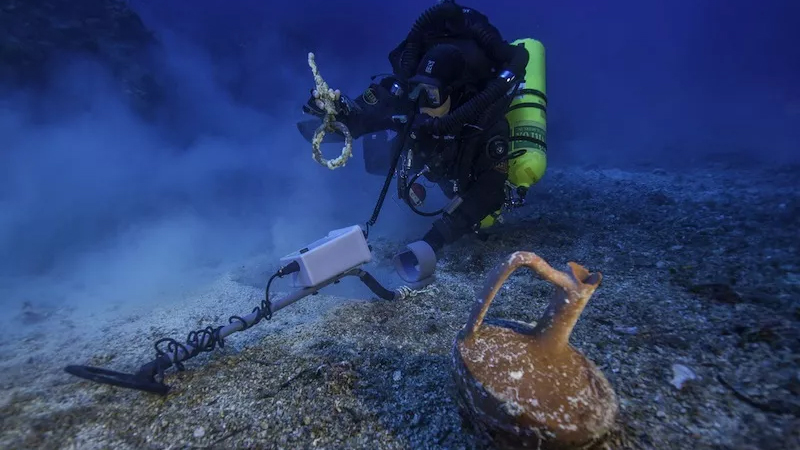

In the course of the 2014 mission, divers made use of rebreather engineering, which recycles air, whilst discovering the Antikythera wreckage. The technology allow the divers keep underwater for up to 3 several hours at a time, so they could dig up artifacts like this lagynos. The lagynos was a unique Hellenistic ware that was applied to pour wine.
Inscriptions discovered

Referred to as fragment 19, this is a piece of the device’s back again protect. Making use of a procedure called polynomial texture mapping, or PTM, researchers could generate a substantially clearer visualization of the Antikythera inscription. With PTM, unique lighting problems can be simulated to reveal floor particulars on artifacts that could normally be hidden.
1st model
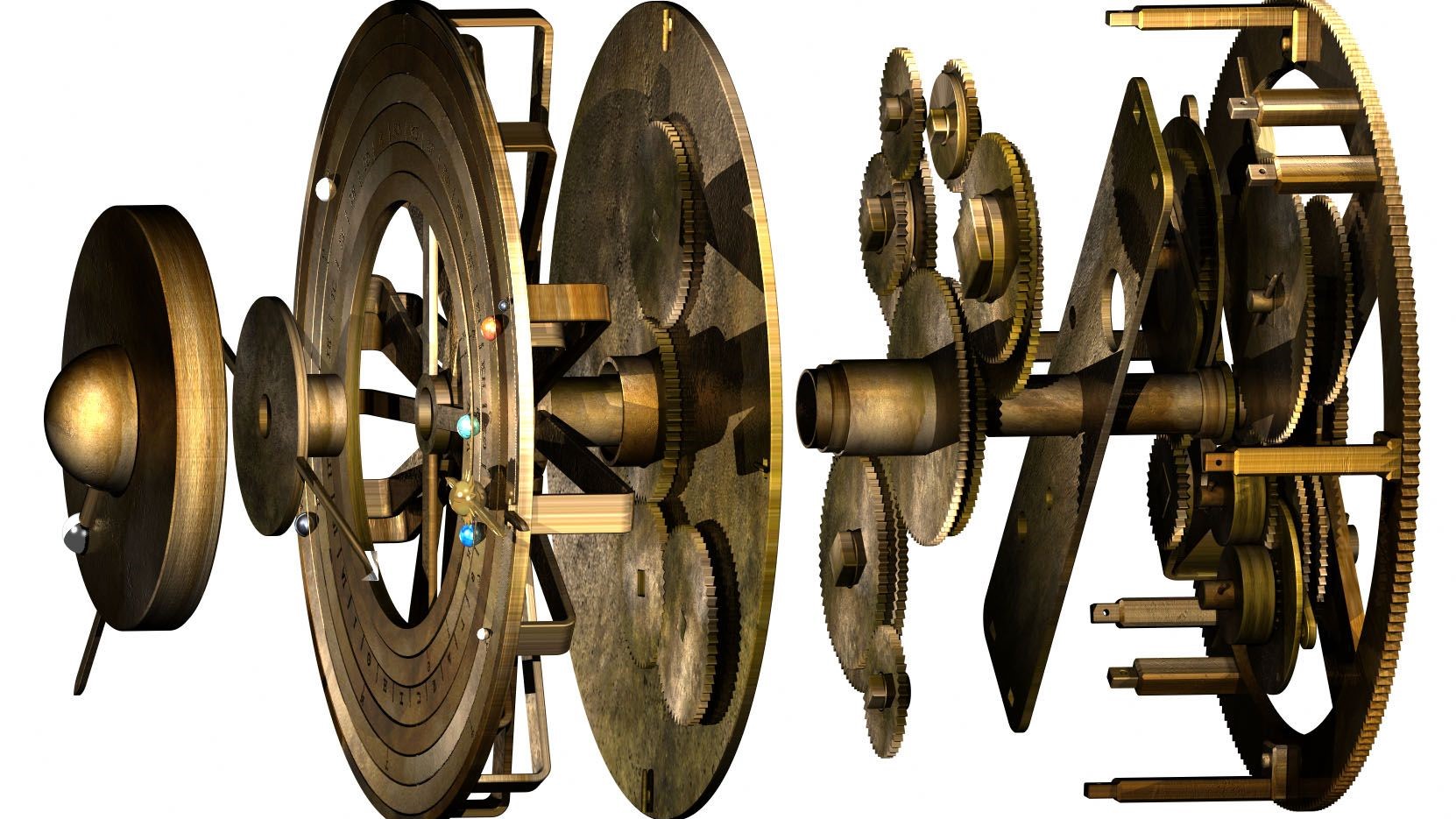
Scientists at College College London described in 2021 that they utilized ancient calculations to completely recreate the style of the Antikythera system. They now hope to piece alongside one another their own contraption centered on the style. Will it function? Each and every gear in the mechanism must chart the movement of a heavenly system.
Within Antikythera
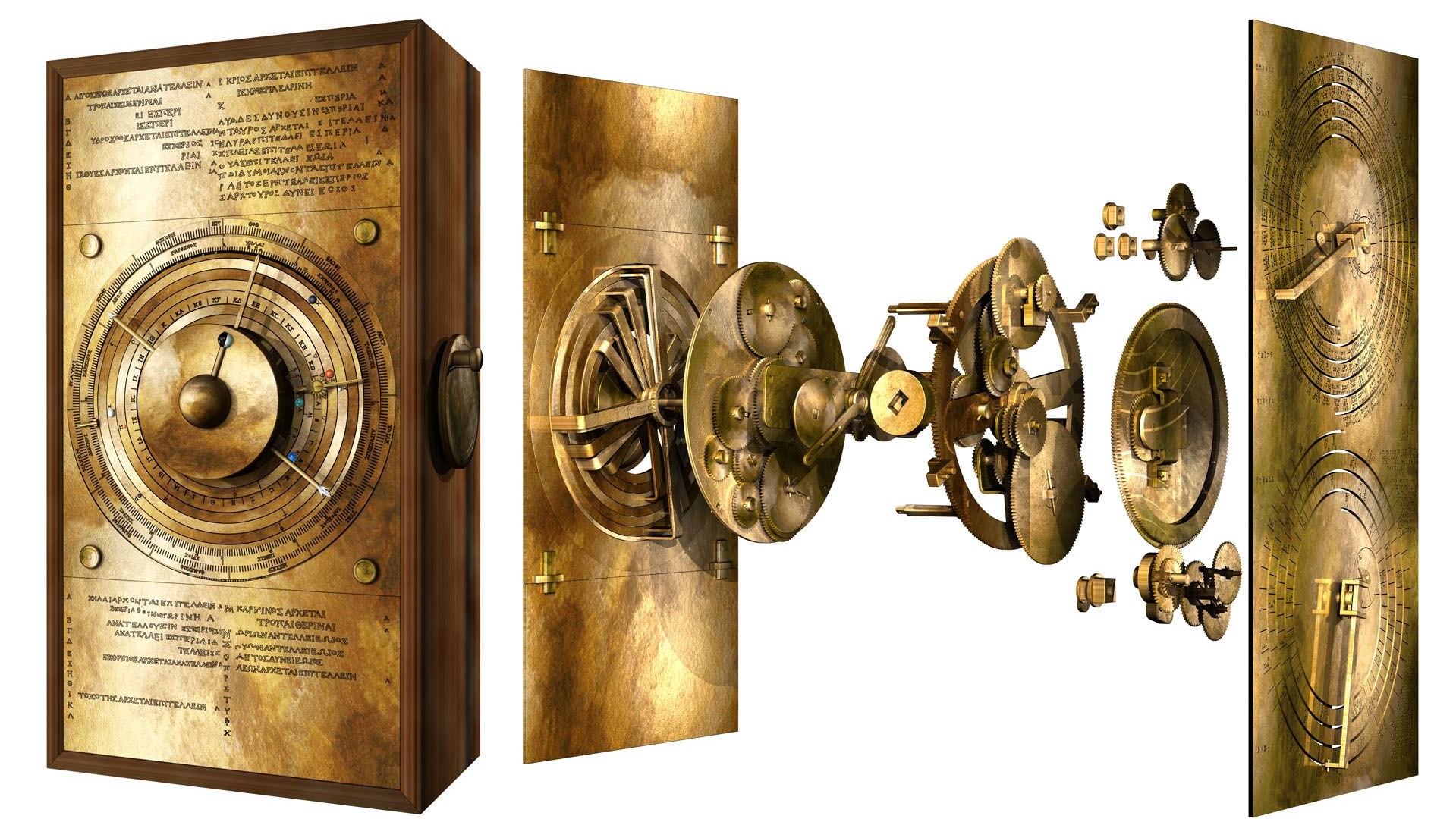

This is what the Antikythera mechanism would have appeared like if pulled aside some 2,000 a long time ago.
At first released on Stay Science.
